For most students, the IB Chemistry IA (Internal Assessment) assignment lurks on the path to academic success like a sphinx with an impossible riddle. The analogy is quite right too, given that the assignments take up a hefty 20% of your total marks in the coursework.
If you are reading this, you are likely confused by the guesswork that surrounds the entire exam. Luckily for you, we at Help for Assessments are old hands at chemistry assignments including IB internal assessments. We will guide you through the process as we debunk the 'nightmare' that is a chemistry IA to make sure you ace it.
If you would love a little more practical help than this detailed guide, our team of experts is at your disposal to carry out your chemistry IA with polished skill. As a multi-faceted team, we are experts in every form of academic writing assignments and projects. Don't be shy, check out our range of services and order your very own writing expert today.
If you still want to proceed, its time you put your apprehension away as we take a practical look into how you can pass the chemistry IA.
This guide will explore the sections and format of a chemistry IA, a look into the marking criteria used, and suggestions at every point to help show you what is expected of you.
What is a Chemistry IA
The IB chemistry IA is an investigative essay that seeks to explain the chemistry behind common real-world phenomena. It seeks to assess your grasp of chemistry up to the level achieved in your coursework through practical application of the skills gained.
Unlike regular test which many students cram their way through, the chemistry IA needs a high level of independent skill, research work, and personal effort to complete.
Coupled with all the other stressful assignments in other subjects, the chemistry IA sometimes feels like an insurmountable problem partly because of the sheer amount of guesswork.
The assignment seeks to develop independent thinking and creative application of concepts learned to the real world. If you can do this successfully, you will earn top marks in the assignment. The first task you have with the chemistry internal assignment is choosing an appropriate topic.
Choosing a Topic for Your Chemistry IA
The first consideration you should take into account when choosing a topic for the IB chemistry IA is that it should be personal. That means it should be one that interests you personally, adapted to your particular cause, and related with a personal touch throughout the text.
To achieve full marks, your topic and essay must meet the conditions set out by the descriptors on IB’s chem page.
However, in the search for authenticity and originality, many students get themselves in a rut trying to invent procedures and experiments. Notice that the paper is looking for independent thinking, creativeness, and initiative.
The best way to achieve these criteria without knocking your brains out is to adapt existing experiments, procedures, or other ideas to your investigation. What you need to showcase is authentic inspiration and highly personalized methods, which you can easily do by adapting existing ones.
Let's say, for example, that you want to investigate the calories in the food you eat. Of course, that is a washed-out idea. How about you give it a new twist and investigate how cooking Ideal Protein packs affects their calorie content? This is something you can do easily with a calorimeter in the lab.
For those who don’t know, Ideal Protein is a popular, albeit shady, weight loss program when dieters substitute daily food for prepackaged ultra-refined protein packets. If you have ever tried it, you can tie it to the investigation to show innovation and inspiration.
The same goes for other common chemistry experiments you will find online, in books, journals, magazines, and other common sources.
With a topic in hand, it's time to plan the investigation and structure it accordingly.
Chemistry IA Format
You will be carrying out the IA assignment in stages, but very little of it will be actual lab work. Most of the work is in the research involved and crafting the actual write up.
So, while we are confident you can handle the actual experimentation (your instructor will be more than glad to help), let us show you how to structure the write up.
There will be seven important parts of the write up, which for the sake of simplicity we will keep calling an essay. The image below will give you a rough idea of how each section appears, but we shall also take a more in-depth look into some of the parts.
Parts of a Chemistry IA
The following image shows a sample structure of a chemistry IA. Please note that it is strictly for guidance only; in no way is it to be taken as a must-use format. Your instructor will usually provide exhaustive instructions in this regard.

Introduction
Your introduction is meant to tell your reader why they should keep reading. Here, give in very brief detail what your experiment is about, why you chose it, and stress your personal connection to the subject matter. You first person ‘I’ or ‘We’ pronouns to achieve this.
a) Background
As part of the Introduction, the background is meant to enhance the reader’s understanding of the context of your investigation. Include a general review of the science behind the concept, backed by facts and evidence.
You can also include the equations and mathematical formulas that you will be using in the assignment.
b) Hypothesis
The hypothesis is meant to be a justification for the choice of science concepts you use to explain the claim under investigation.
More technically, it should be a specific prediction about the outcome of your experiment or how the dependent variable will change with the independent one.
For example, with our example, our hypothesis might be:
“Using calorimeters to find out whether Ideal Protein packs change in calorie content value upon cooking in various ways.”
Design
In any other discipline, this section would probably be called ‘methodology’ or ‘procedure.’ This is the part where you tell, in complete detail, how you carry out your experiment.
a) Research Question
The design part starts with a research question in the form ‘how is x dependent on Y?’ It should be a highly specific question outlining the variance you are investigating, stated without any ambiguity.
b) Variables
Outline fully what your variables are, outlining the three types:
c) Method
As part of the design, the method or procedure is a detailed explanation of how you carried out the experiment or tests required to measure the variables. No matter how strong the temptation is, do not take this section off a chemistry book or lap report.
Most students trip on this section because they forget the procedure is supposed to be specially adapted and personalized for this assessment.
If you were choosing a reagent, state why you chose it. If you are choosing a flask, show the reasoning behind your choice. For example, 'use a glass stirring rod instead of a metallic one to prevent reaction with the reagent …'
It is also a good idea to include a diagram of your setup and describe any modifications you had to improvise. A picture will also do.
Results
a) Raw Data
Record your data as soon as you collect it. This is usually done in tables where you can compare the variables easily and fill in the gaps quickly. You need to collect both quantitative (measured, e.g. 10g of residue) and qualitative data (observed, e.g. color change, bubbles).
Report every measured value and include every field on the same table where possible. If any of the data values don't match, you can enter it in different fields.
b) Analysis
Use your measured data to calculate totals, averages, correlations, among others. Draw graphs and charts as needed. Be sure to show the entirety of your working including the formulas you used. Note any uncertainties and margins of error expected.
If you have an accepted value for that kind of experiment, compare the two and see how close they come to each other. If you have graphs, make them appealing, give them names, and name them accordingly.
Conclusion
The conclusion should be a rewording of your research question to give an answer based on the trend observed and proved by your results. The conclusion is a three-part section that also includes:
a) Evaluation
The evaluation is a critical review of your methods and how well the procedure you chose worked to your benefit (or not). If there are any discordant data/outlier points, discuss them here.
b) Improvements
Suggest any improvements or changes you would make if you were to repeat the experiment. What would you advise anyone else using the same procedure for the experiment? Do you have any suggestions to make it better?
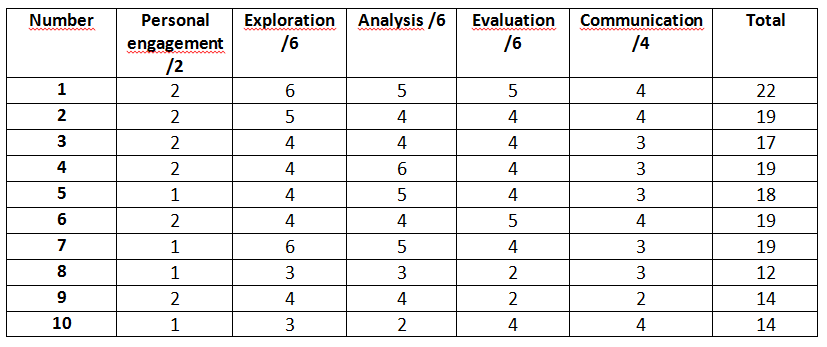
Marking Criteria for Your Chemistry IA
By now, you can tell that personal engagement is a pretty big deal in your chemistry IA, but it is not the only one.
Markers will rely on several other criteria to grade your work, including:
1. Exploration
Exploration is a measure of how well you establish a scientific context for the project. It measures how well focused and grounded your research question is, as well as your awareness and knowledge of safety, environmental, and ethical concerns involved, if any.
2. Methodology
This criterion measures how clearly and thoroughly you set out your procedure. You should have at least 5 variations or manipulations of the independent variable and 3 trials for each.
You should collect as many significant data points as possible, set out any safety procedures taken, and qualify each choice of equipment and supplies.
3. Analysis
This metric measures your data collection, organizational, and presentation skills. All calculations must be shown clearly, formulas displayed, and all qualitative and quantitative data recorded.
4. Evaluation
This metric contributes 6 marks to the total 20 and assesses how well the results obtained serve to prove/disprove your research question in the accepted context.
You also get points for suggesting useful improvements, noting and owning up to any weakness of the methodology, and describing the strength of the correlation between the results and the hypothesis.
5. Communication
This criterion is a measure of how clearly and effectively you presented yourself in the essay.
6. Personal Engagement
As discussed, you will need to completely own the entire project from start to finish. Choose every word with care, especially if you use textbook sources along the way. Cite each of these appropriately because, needless to say, plagiarism is a capital crime in the assessment.
Need Help With Your Chemistry IA Assignment?
Many students are tempted to rush through with the assignment to be ‘over and done with’ it. However, such IB assessments are tricky because they test not only the outcomes, but also the process, the student’s state of mind, and the overall circumstances surrounding the assessment.
If you truly want to be 'over and done with' the assignment, the only way to do it is to be diligent and do it as meticulously as you can. However, you can also hand over the entire problem to chemistry internal assessment experts at Help for Assessments to write it for you.
With years of experience and skill in the market, we will take the burden off your hands and do the entire assessment for you in record time and at the lowest prices. If you want to experience total peace of mind, order our stellar services here. We are here for you, always.